Olive oil: A superfood source of antioxidants and heart-healthy fats
04/17/2025 / By Laura Harris
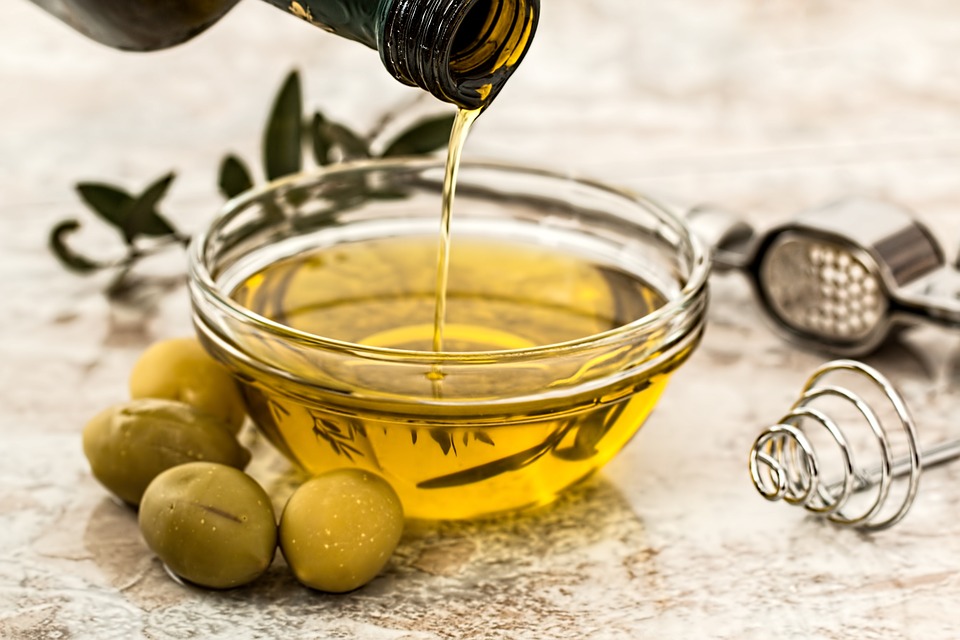

- Olive oil, particularly extra-virgin (EVOO), is high in monounsaturated fats (oleic acid) and polyphenols that can reduce inflammation, improve heart health and combat oxidative stress.
- Studies link olive oil to lower risks of heart disease, stroke, depression, breast cancer and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s due to its antioxidant properties.
- Cold-pressed organic EVOO retains the most nutrients; avoid refined or adulterated oils (mixed with cheaper oils like soybean). Store in opaque containers to prevent light damage.
- EVOO can handle moderate heat (up to 375 F) but is best for low-heat cooking, dressings and finishing dishes. Avoid high-heat frying to preserve antioxidants.
- Non-organic olive oil may contain pesticides (like glyphosate) or heavy metals. Organic certification ensures cleaner, toxin-free production for maximum health benefits.
Olive oil has long been celebrated as a cornerstone of health and culinary excellence. Originating in the Mediterranean, this golden elixir is more than just a cooking staple – it is a potent superfood packed with antioxidants, healthy fats and disease-fighting compounds. From ancient medicinal uses to modern dietary recommendations, its benefits have stood the test of time.
History and origin of olive oil
Olive oil is derived from the fruit of the olive tree (Olea europaea), primarily cultivated in the Mediterranean basin. Spain, Italy, Greece and Turkey dominate global olive oil production. Its use dates back over 6,000 years, with evidence of olive oil extraction found in ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt. The Greeks and Romans valued it for cooking, skincare and even religious ceremonies.
Today, olive oil has become a global commodity, particularly after World War II, when researchers identified the “Mediterranean Diet” as one of the healthiest eating patterns in the world. Extra virgin olive oil, the least processed form, is now a dietary mainstay for health-conscious consumers.
Nutritional profile and health benefits
Olive oil’s health benefits stem from its impressive nutrient composition:
Healthy fats (monounsaturated fatty acids – MUFAs)
- Primarily oleic acid, which reduces inflammation and supports heart health.
- Helps lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol while increasing HDL (“good”) cholesterol.
Antioxidants (polyphenols and vitamin E)
- Polyphenols such as oleocanthal (with anti-inflammatory effects similar to ibuprofen) and hydroxytyrosol fight oxidative stress.
- Vitamin E protects cells from free radical damage, promoting skin and immune health.
Other beneficial compounds
- Squalene – A natural compound that may help prevent cancer and support skin hydration.
- Phytosterols – Plant compounds that help block cholesterol absorption in the gut.
These nutrients make olive oil a key player in preventing chronic diseases, from cardiovascular conditions to neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s.
Scientific research overwhelmingly supports olive oil as a highly beneficial food, especially when used daily. Unlike other cooking oils, it has been linked to a lower risk of heart disease and obesity. To get the best benefits, experts recommend choosing organic, cold-pressed extra virgin olive oil, as processed or low-quality oils may lack nutrients or contain harmful additives.
However, its health advantages depend on an overall balanced diet rich in fresh fruits, vegetables, fish and nuts, which provide antioxidants that protect against chronic diseases. Simply adding olive oil to an unhealthy diet may not provide the full benefits. (Related: 8 Science-based health benefits of olive oil.)
Moreover, some brands mix olive oil with cheaper oils (like soybean or canola), reducing its nutritional value. Olive oil can also handle moderate cooking temperatures (375 F for extra virgin, 465 F for refined), so excessive heat can degrade its antioxidants.
Like all oils, olive oil is high in calories, so portion control is important for weight management.
Despite these concerns, when consumed wisely, olive oil remains one of the healthiest fats available. Choosing high-quality versions and using them as part of a nutritious diet maximizes its benefits.
Why choose organic
Choosing high-quality organic olive oil helps avoid harmful pesticides and contaminants. While olives naturally require fewer pesticides than crops like celery, peaches or strawberries (which can contain 47–67 pesticides per serving), conventional olive farming may still use neurotoxic chemicals like chlorpyrifos and glyphosate, linked to Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
Organic certification ensures no synthetic pesticides are used. Additionally, some olive oils may contain traces of heavy metals like lead or arsenic from soil contamination, so reputable producers test for these. For the safest and healthiest option, opt for cold-pressed, extra virgin, organic olive oil.
Culinary uses of olive oil
Olive oil’s versatility shines in countless recipes. Here are some classic and modern ways to use it:
Dressings and dips
- Traditional Greek salad dressing (olive oil, lemon juice, oregano)
- Hummus (blended with chickpeas and tahini)
- Bruschetta topping (olive oil, tomatoes, garlic, basil)
Cooking and sautéing
- Sautéed greens (spinach, kale or Swiss chard)
- Roasted vegetables (drizzled before baking)
Baking and frying
- Olive oil cakes (a moist, Mediterranean-style dessert)
- Light frying (for dishes like falafel or fish)
Finishing touches
- Drizzled over soups (like gazpacho) or pasta
- Bread dipping oil (mixed with herbs and balsamic vinegar)
This story is not medical advice and is not intended to treat or cure any disease. Always consult with a qualified naturopathic physician for personalized advice about your specific health situation or concern.
Explore more about the health benefits of superfoods like olive oil and other natural ingredients at NaturalNews.com, your trusted source for wellness insights and nutritional knowledge.
For cutting-edge tools to expand your understanding of natural health, try Brighteon.ai, an innovative AI model created by Mike Adams, the Health Ranger. This free, downloadable tool is designed to decentralize knowledge, bypass censorship, and empower individuals with actionable information.
If you’re passionate about nutrition, natural medicine, and uncensored discussions, visit Brighteon.com and a free speech video platform and join our vibrant communities on Brighteon.IO and Brighteon.social. Dive into open conversations about food, ingredients and holistic health today!
Watch the video below to learn how olives can help protect against liver disease.
This video is from the Groovy Bee channel on Brighteon.com.
More related stories:
Olive oil really is the healthiest oil for frying foods, scientists find.
How extra virgin olive oil protects against Alzheimer’s.
Olive oil helps prevent visible facial skin aging.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
food cures, food is medicine, food science, functional food, grocery cures, health science, heart health, ingredients, natural cures, natural health, natural medicine, nutrients, nutrition, olive oil, organics
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
Natural.News is a fact-based public education website published by Natural News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Natural News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.